Waste management automation refers to the use of technology to streamline – waste collection, sorting, recycling, and disposal.
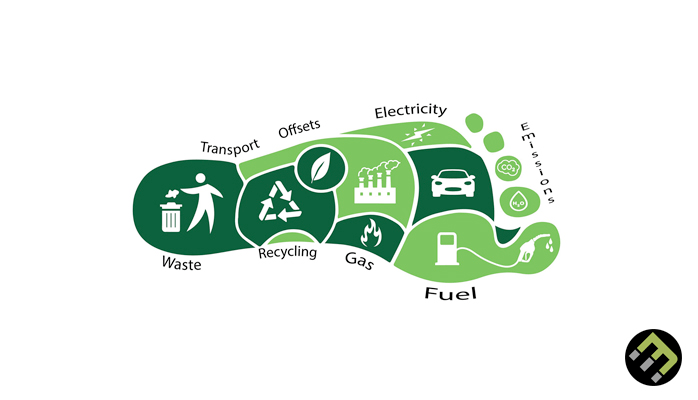
This reduces the carbon footprint associated with waste management processes. The various technological interventions can be stated as below:
- Optimized Collection Routes: Automated systems can analyze data and optimize waste collection routes, ensuring that collection vehicles take the most efficient paths. This reduces fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to lower carbon emissions.
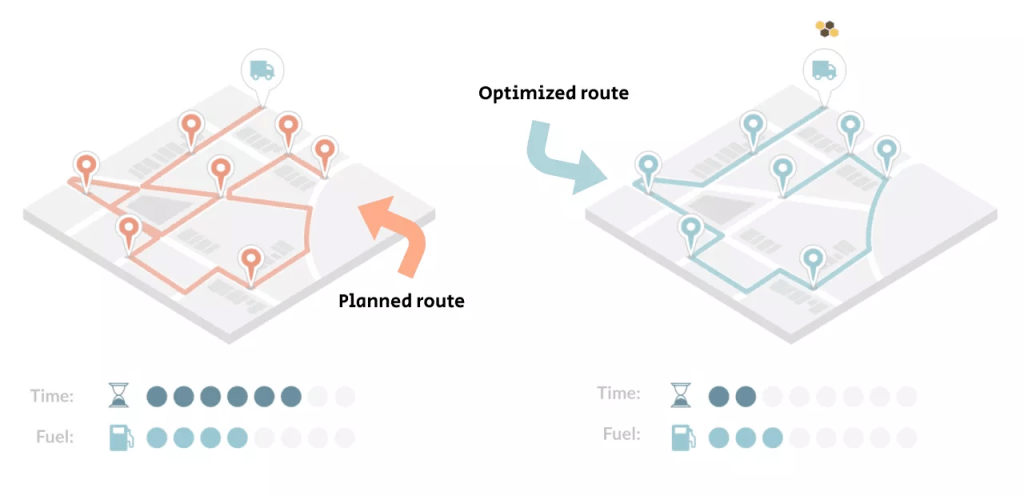
- Sensor-Based Sorting: Automated sorting technologies, such as sensor-based systems and robotics, can improve the efficiency and accuracy of sorting materials for recycling. This reduces the need for manual labor and ensures that more materials are recycled, reducing the energy and emissions associated with the production of new materials.

- Smart Bins: IoT (Internet of Things) technology can be integrated into waste bins to monitor their fill levels. This data can be used to optimize collection schedules, preventing unnecessary trips and reducing fuel consumption.

- Energy Recovery: Automated waste-to-energy processes can efficiently convert certain types of waste into energy. This not only helps in waste reduction but also provides an alternative energy source, potentially displacing the need for energy derived from fossil fuels.
With the above steps incorporated, the impact will be multi-fold as it will aid in
- Reduced Landfill Usage: By increasing recycling rates and implementing waste-to-energy technologies, waste management automation can help reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. Landfills emit methane, a potent greenhouse gas, so minimizing landfill usage contributes to lower overall carbon emissions.
- Informed Decision Making: Big data analytics can be employed to analyze patterns and trends in waste generation that will allow in targeted efforts to reduce waste at the source and implement more effective recycling programs.
- Cost Savings: Minimal physical presence, reduced operational costs (travel-related associated with on-site management and maintenance activities).
- Lifecycle Analysis: Tracking and analysis of the entire lifecycle of materials will reduce environmental impact and carbon footprint.
Waste management automation can contribute to carbon footprint reduction but for overall effectiveness a holistic approach that combines technology, public awareness, and supportive policies is essential for lasting reductions.

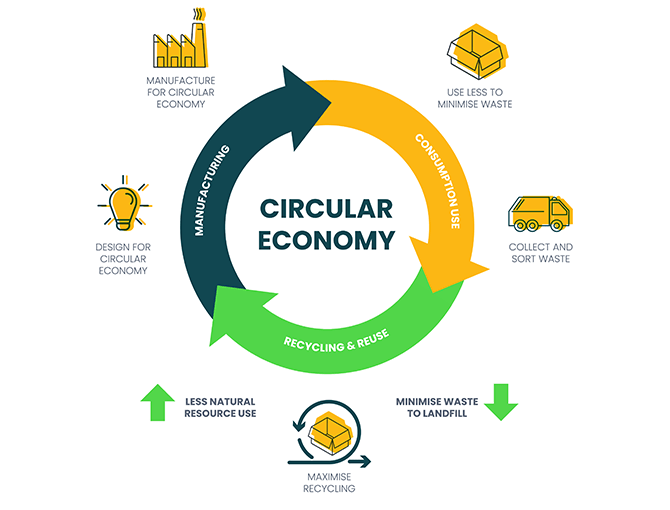
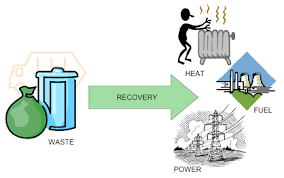
This is very nicely explained. Very insightful 👌
LikeLike