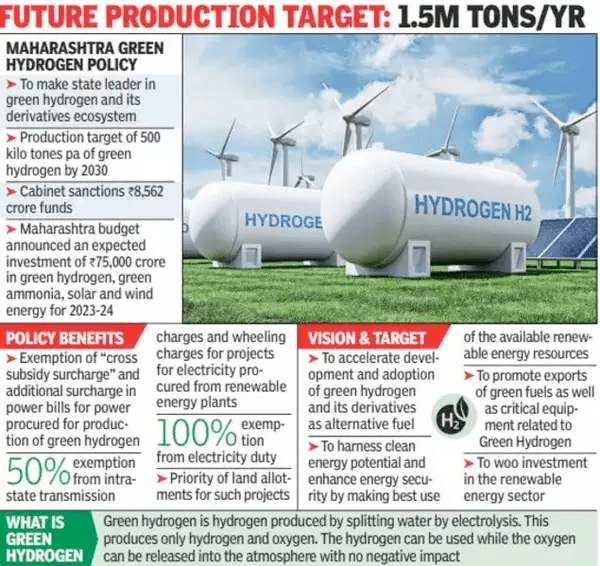
Hydrogen-based transportation holds promise as a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
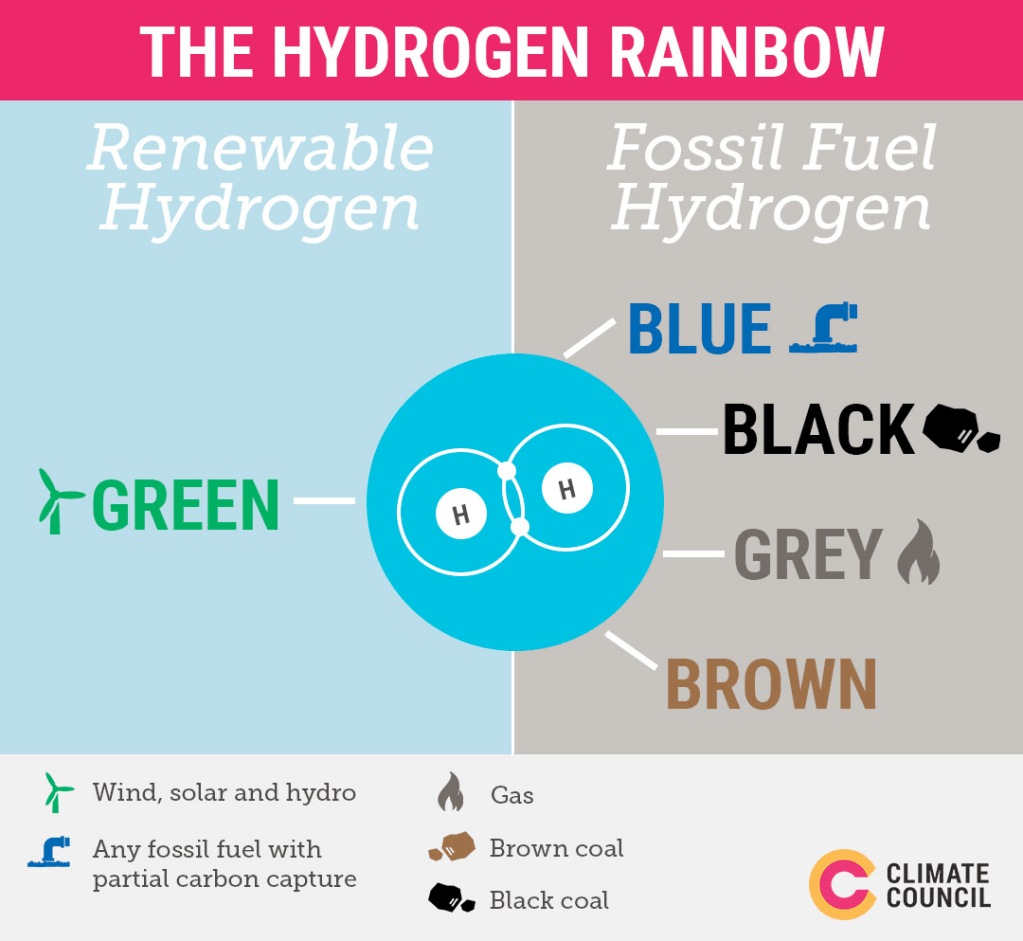
Despite the promise, the technology-policy-awareness gap exists for it to be adopted on a mass scale.
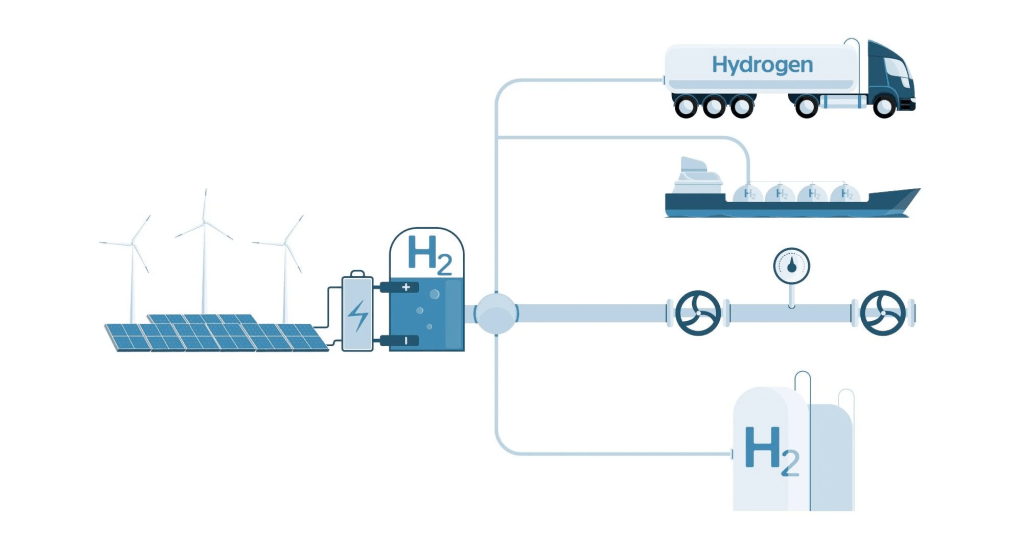
The list below shares the challenges in some detail for better appreciation of the steps to be overcome before widespread adoption kicks-in:
Current Production Approach
Hydrogen is currently produced from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming (SMR), which emits carbon dioxide.

Green Hydrogen production methods, such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy is still evolving. Improving the durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness of fuel cells is essential for making hydrogen-powered vehicles more practical.

Infrastructure Side Challenges
Hydrogen has a low energy density per unit volume, making storage and transportation challenging. Developing efficient and safe storage methods, such as advanced composites or solid-state storage, is crucial.
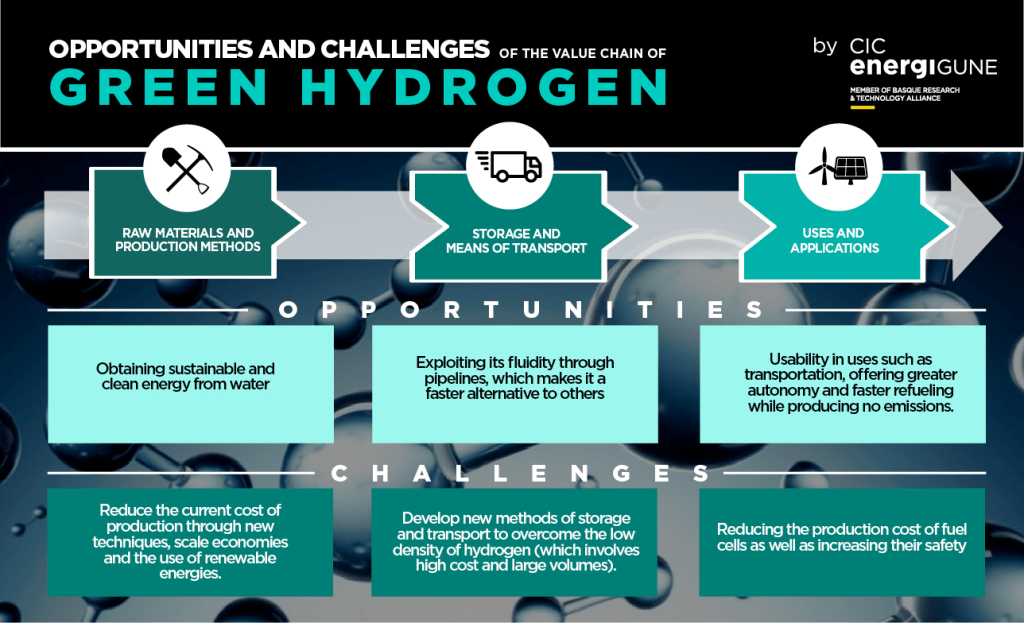
Regulatory Support
Governments need to implement supportive policies, incentives, and regulations to encourage investment in hydrogen infrastructure and technology.
Economic Viability
Achieving economic viability is essential for the widespread adoption of hydrogen-based transportation. The cost of hydrogen vehicles and their components, such as fuel cells, needs to be competitive with traditional vehicles to attract consumers and businesses.

Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from governments, industries, and research institutions for potential of hydrogen-based transportation as a sustainable and scalable solution for the future.
If you find this helpful, please feel free to share it with others
You can follow my blog or Facebook page for getting insight on other topics.