Introduction:
Hydrometallurgical processes use aqueous solutions to extract and recover metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled materials, including e-waste[1][2][3].
Process Flow:
The process typically involves three main steps:
- Leaching: Metals are dissolved from solids into a solution using acids, bases, or other chemicals
- Solution purification: The solution is treated to separate and concentrate the desired metals
- Metal recovery: Metals are recovered from the purified solution, often by electrolysis or precipitation[1][2]
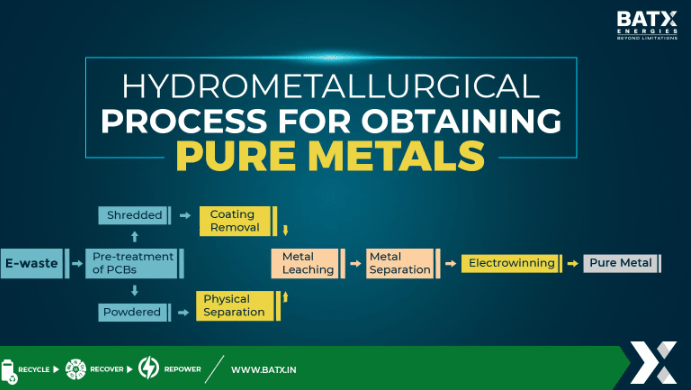
Applications of Hydrometallurgy:
- Extraction of metals like copper, gold, uranium, and rare earth elements from ores[1][4]
- Recycling of electronic waste (e-waste) to recover precious and base metals such as gold, silver, copper, and rare earths[5][4][6]
- Battery recycling to reclaim lithium, cobalt, and nickel from spent batteries[4][7]
- Recovery of metals from industrial by-products and spent catalysts[5]
Benefits for E-Waste Recycling and Carbon Footprint Reduction:
- Hydrometallurgical processes are crucial for efficiently recovering valuable metals from e-waste, reducing the need for primary mining and conserving natural resources[5][6][8]
- These processes generate less air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional high-temperature (pyrometallurgical) methods, thereby helping reduce the carbon footprint of metal production and recycling[7][8]
- By enabling the circular use of metals, hydrometallurgy supports sustainable resource management and the development of a circular economy[7][8]
Summary
Hydrometallurgy is a versatile and environmentally friendly approach for metal extraction and recycling, especially valuable in addressing the challenges of e-waste and climate change[5][7][8].
References:
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrometallurgy
[2]https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/University_of_Missouri/MU:_1330H(Keller)/23:_Metals_and_Metallurgy/23.3:_Hydrometallurgy
[3] https://www.basf.com/us/en/media/smart-scientists/hydrometallurgy
[4] https://www.stonex.com/en/financial-glossary/hydrometallurgy/
[5] https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access-pdfs/hydrometallurgy-principles-processes-and-applications.pdf
[6] https://www.sustainablemanufacturingexpo.com/en/articles/advancements-electronic-waste-recycling.html
[7] https://climate.sustainability-directory.com/term/hydrometallurgical-processes/
[8] https://prism.sustainability-directory.com/term/e-waste-hydrometallurgy/
[9] https://gurumuda.net/metallurgy/process-and-applications-of-hydrometallurgy.htm
[10] https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/hydrometallurgical-process
[11] https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10643389.2020.1847949
[12] https://www.purolite.com/dam/jcr:3fc1fd51-bef0-4406-803f-e85e3bb83160/PT%20Hydrometallurgy%20Application%20Guide.pdf
[13] https://energy.sustainability-directory.com/area/hydrometallurgical-processing/
[14] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128161906000108
[15] https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781119891543.ch18
[16] https://pcacom.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/10.1016@B978-0-12-816190-6.00010-8.pdf
[17] https://www.guanmamachinery.com/what-is-the-meaning-of-hydrometallurgical/
[18] https://energy.sustainability-directory.com/term/hydrometallurgical-process/
[19] https://energy.sustainability-directory.com/term/hydrometallurgical-processes/
[20] https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/hydrometallurgy-extractive-metallurgy-ultimate-guide
[21] https://doaj.org/article/6ef8146068a445f29d9386434f4f31d7
[22] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-67507-7
[23] https://www.hydro.com/en/global/media/news/2020/carbon-neutral-by-2020-done/


Leave a comment