Introduction
Sodium-ion batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that uses sodium instead of lithium to store and release energy. In simple terms, they work very much like lithium-ion batteries, but with a different raw material.
Sodium is the same element commonly found in salt, and it is widely available across the world.
How Do Sodium-Ion Batteries Work?
Every battery has three basic parts:
- Anode (one side)
- Cathode (the other side)
- Electrolyte (the medium between them)
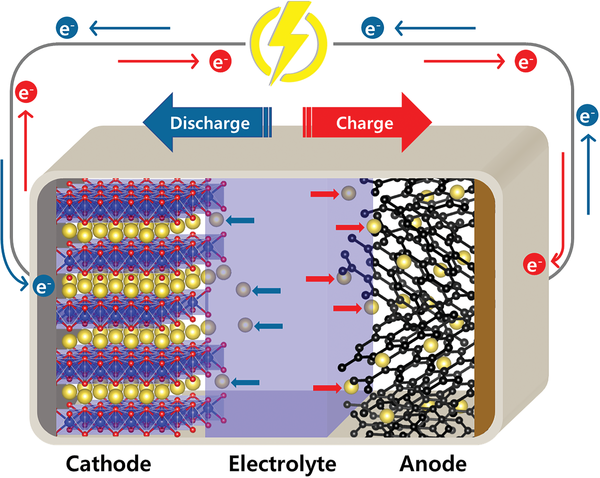
Movement of ions = electricity for your device.
- When the battery is charging, sodium ions move in one direction.
- When the battery is in use, these ions move back, releasing electricity.
Why Are Sodium-Ion Batteries Being Talked About?
1. Sodium Is Easily Available
Lithium is limited and concentrated in a few countries. Sodium, on the other hand, is abundant and inexpensive. This makes sodium-ion batteries less dependent on rare resources.

2. Lower Cost
Because sodium is cheaper than lithium, these batteries have the potential to reduce overall battery costs, especially for large-scale storage.
3. Better for Stationary Energy Storage
Sodium-ion batteries are well-suited for:
- Solar power storage
- Wind energy storage
- Backup power for grids and buildings
They may not replace lithium everywhere, but they fit very well in these use cases.
How Are Sodium-Ion Batteries Different from Lithium-Ion?
| Aspect | Sodium-Ion | Lithium-Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Raw material | Abundant | Limited |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Energy density | Slightly lower | Higher |
| Best use | Grid & storage | Mobiles, EVs |
Are Sodium-Ion Batteries Used Today?
They are still in the early adoption stage, but:
- Pilot projects are running
- Energy storage companies are testing them
- Countries looking to reduce battery import dependence are showing interest
Over time, their presence is expected to grow, especially in renewable energy systems.
Final Thoughts
Sodium-ion batteries are not a replacement for lithium-ion, but a strong alternative where cost, availability, and large-scale storage matter more than size.
As renewable energy expands and energy storage becomes critical, sodium-ion batteries could play a quiet but important role in the future energy ecosystem.

Leave a comment